A Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) is a unique identifier assigned to entities that engage in financial transactions. It is a 20-character alphanumeric code that is used to uniquely identify legally distinct entities that participate in financial transactions. The LEI system was introduced as a global standard to enhance transparency in financial markets and help regulators and businesses better manage financial risks.
This is to inform you that RBI with circular dated Dec 10, 2021 has introduced the Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) which is a 20-digit number used to uniquely identify parties to financial transactions worldwide to improve the quality and accuracy of financial data systems. Additionally, RBI is introducing fields/options containing LEI numbers for resident entities and non-resident counterparts in both Inward Remittance Messages (IRMs) and Outward Remittance Messages (ORMs) to be reported in EDPMS/IDPMS.
As per RBI’s Directions, the Bank is required to obtain Legal Entity Identifier (‘LEI’) number from all resident entities (non-individual) undertaking Capital or Current Account transactions of ₹50 crore and above (per transaction) under FEMA, 1999 with effect from Oct 01, 2022.
The Bank has received another direction from RBI dated Oct 25, 2023 stating that the new format of regularisation of bills will have the LEI number as a mandatory field. If the same is not filled, bills will not be regularised. Provide the LEI number and refer to the below limits while undertaking transactions:
| Sr. No. | Type of Transactions | Limit for LEI Number Applicability (per Transaction) |
| 1 | Cash, Tom and Spot Forex Transactions | Amount equivalent to or exceeding USD 1 million or equivalent thereof |
| 2 | Capital or Current Account Transactions under FEMA, 1999 | Amount equivalent to or exceeding ₹50 crore |
You may obtain LEI from any of the Local Operating Units accredited by the Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation. In India, LEI can be obtained from Legal Entity Identifier India Ltd. available at https://www.ccilindia-lei.co.in
Here are some key points about Legal Entity Identifiers:
- Global Standard: LEIs are standardized globally, and the system is overseen by the Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation (GLEIF). The GLEIF ensures the quality and uniqueness of LEIs.
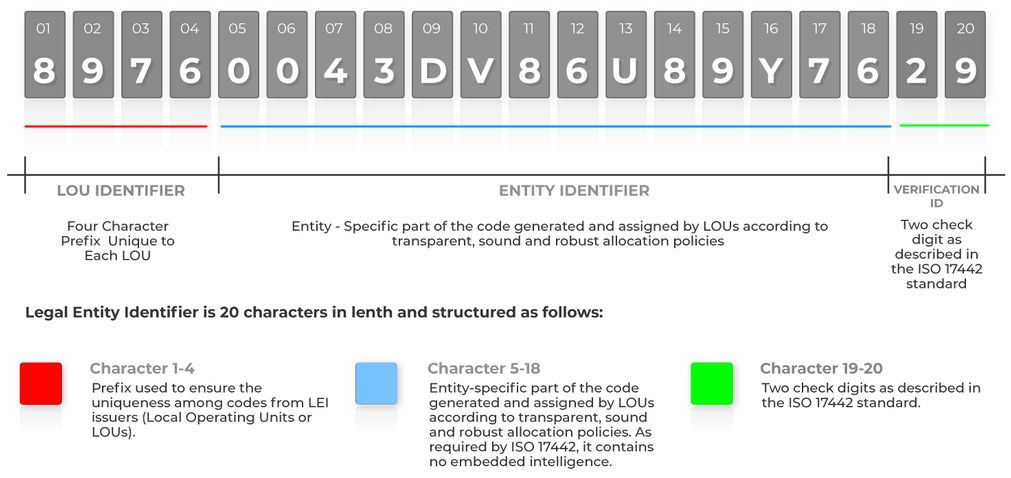
- Structure: The LEI is a 20-character alphanumeric code, with the first four characters representing the LEI issuer code, followed by 12 characters that uniquely identify the legal entity, and the last two characters being checksum digits.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of the LEI is to provide a standardized and unique identifier for legal entities engaging in financial transactions. This helps regulators and market participants track and analyze financial transactions and connections between entities.
- Regulatory Requirement: In many jurisdictions, the use of LEIs is a regulatory requirement for entities engaging in financial transactions. This is to enhance transparency, reduce systemic risk, and improve the ability to monitor and manage financial exposures.
- Who Needs an LEI: Entities such as corporations, banks, investment funds, and other legal entities involved in financial transactions typically need to obtain an LEI. This includes entities engaged in activities like trading financial instruments, issuing securities, or participating in derivative transactions.
- Registration Process: Obtaining an LEI involves a registration process with an authorized LEI issuer. These issuers are organizations that have been accredited by the Global LEI System to issue and maintain LEIs.
- Renewal: LEIs need to be renewed annually to ensure that the information associated with the legal entity is up to date.
The use of LEIs has become increasingly important in the financial industry to facilitate better risk management, regulatory compliance, and overall transparency in global financial markets.